TEHRAN, Iran // The human impact from the wrangling between Iran and the West over its nuclear program could fall first in nuclear medicine clinics around the country, where hundreds of cancer patients a week get treatment with radioactive isotopes.
Iran says fuel for the Tehran research reactor that produces the isotopes will run out in September next year, leaving it without the materials needed to diagnose and treat some 850,000 cancer patients across the country.
A deal for the West to provide fuel for the reactor has all but fallen apart in the deadlock over Iran's broader nuclear program, and Iran's drive to produce the fuel on its own has brought condemnation from the US and Europe. They fear the program could boost what they contend is the secret goal of Iran's nuclear ambitions: to produce a bomb.
Iran denies the claim, saying its program is only for peaceful purposes and has touted the need for medical isotopes to justify its program.
Negotiators from Iran and the United States and its allies are expected to meet soon - likely late this month or early next - in their first direct nuclear talks in more than a year. A deal to provide Iran with fuel for the research reactor may be on the agenda - but US officials have already expressed pessimism that one can be reached.
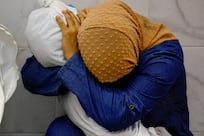
At the nuclear medicine ward in Tehran's Shariati Hospital, Ghodratollah Ghalavand fears the standoff could eventually leave him without his lifeline. Every week, he comes in for treatment of his thyroid cancer with iodine-131 isotopes produced by the reactor.
"I'm not familiar with politics. I'm a rural person. I only know that not giving fuel is wrong. It will endanger my life. Humanitarian issues are different from politics," said Mr Ghalavand, a man in his 50s from a village in southwest Iran.
The Tehran reactor is fueled by rods made from uranium that has been enriched to a level of 20 per cent. It has been running on fuel rods that Iran imported from Argentina more than a decade ago to produce medical isotopes like iodine-131, used to treat thyroid cancer.
Iran imports some ready-made isotopes, but it has faced greater restrictions under UN sanctions and has to pay higher prices to get them. Sanctions do not directly ban the sale to Iran of medical equipment, but they make foreign producers more reluctant to provide it, and those who will sell it do so at inflated prices.
"We are paying twice the value of this product to import it from Turkey," said Mohammad Reza Ramezani, an official at Shariati Hospital, pointing to a cargo of technetium-99, the most common radioisotope used in diagnosis, that arrived from Turkey at day earlier.
Uranium enrichment lies at the heart of Iran's dispute with the West. Low-enriched uranium - at around 3.5 per cent - can be used to fuel a reactor to generate electricity, which Iran says is the intention of its program. But if uranium is further enriched to around 90 percent purity, it can be used to develop a nuclear warhead.
Iran has been producing low-enriched uranium for several years, but the United Nations has demanded that it stop enrichment for fear it will be increased to weapons-grade. The UN has imposed four rounds of financial sanctions on Iran for refusing the demands.