Ethiopians will vote on Monday in a landmark election overshadowed by reports of famine in the country's war-hit Tigray region and beset by logistical problems that mean some people wil not be able to vote until September.
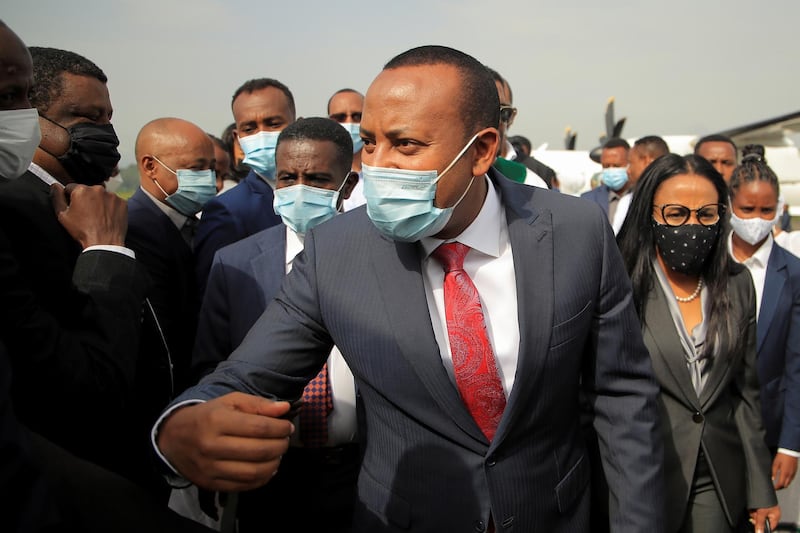
The election is the centrepiece of a reform drive by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed, whose rise to power in 2018 seemed to signal a break with decades of authoritarian rule and led to him being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize the following year. He described the poll as "the nation's first attempt at free and fair elections".
Mr Abiy’s ruling Prosperity Party, formed in 2019 by merging groups who made up the previous ruling coalition, is widely expected to cement its hold on power. The party that wins a majority of seats in the House of Peoples’ Representatives will form the next government.
“We will secure Ethiopia’s unity,” Mr Abiy said ahead of his final campaign rally on Wednesday, repeating his vow of a free and fair election after past votes were marred by allegations of fraud.
But opposition groups accuse Ethiopia's ruling party of harassment, manipulation and threats of violence that echo abuses of the past.
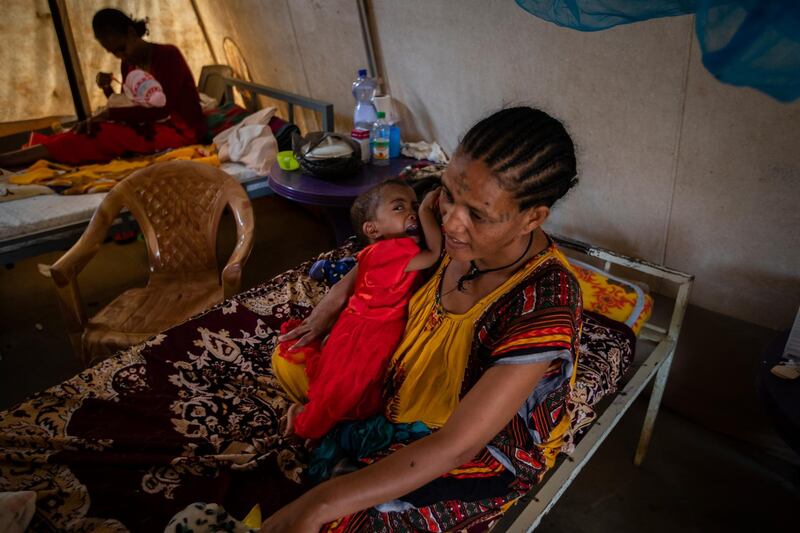
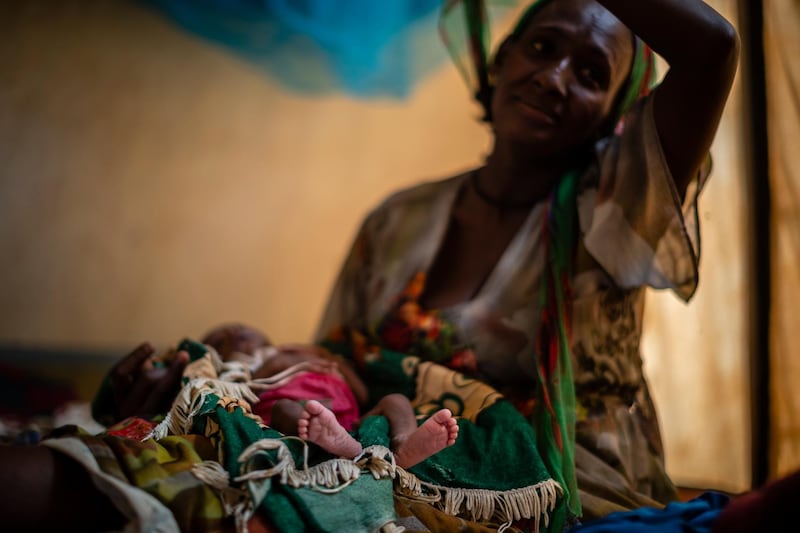
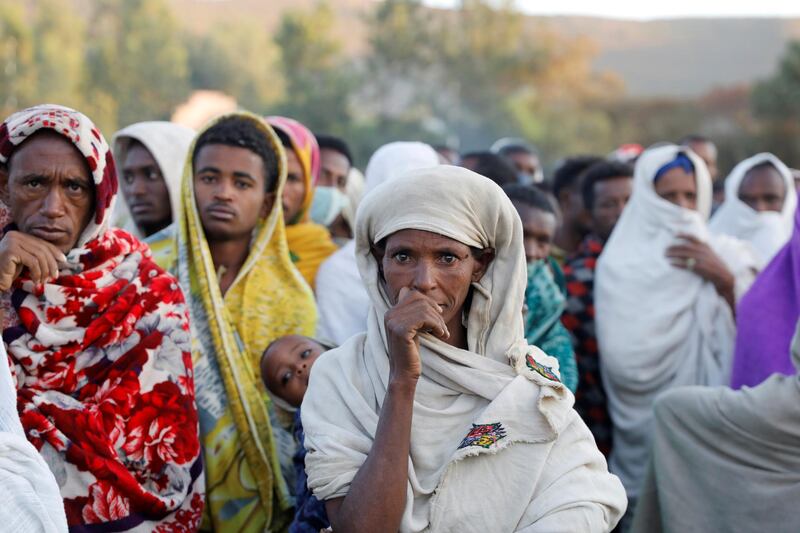
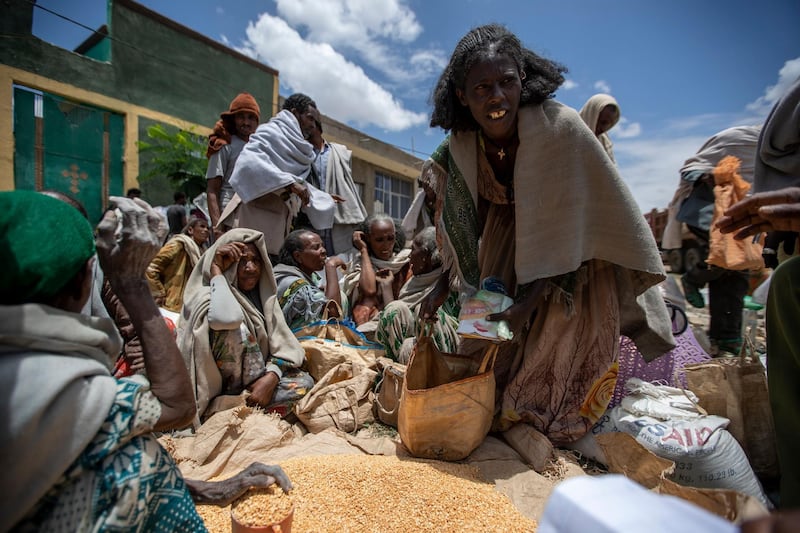
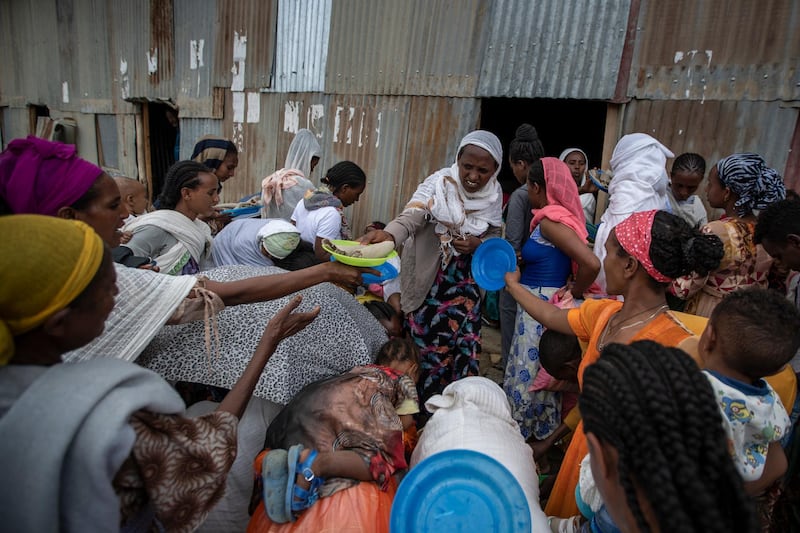
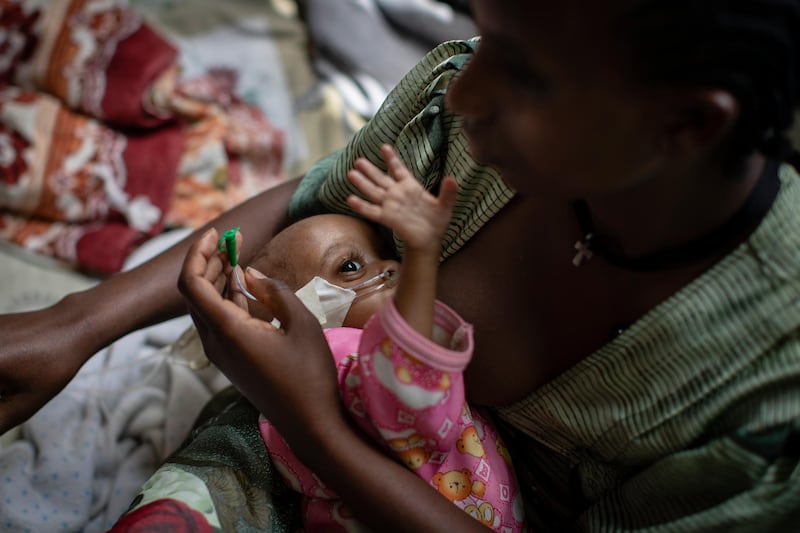
Mr Abiy is facing growing international criticism over the war in Ethiopia's northern Tigray region. Thousands of civilians have been killed and more than two million people displaced since fighting broke out in November between Ethiopian forces, backed by fighters from neighbouring Eritrea, and those supporting the now-fugitive Tigray leaders.
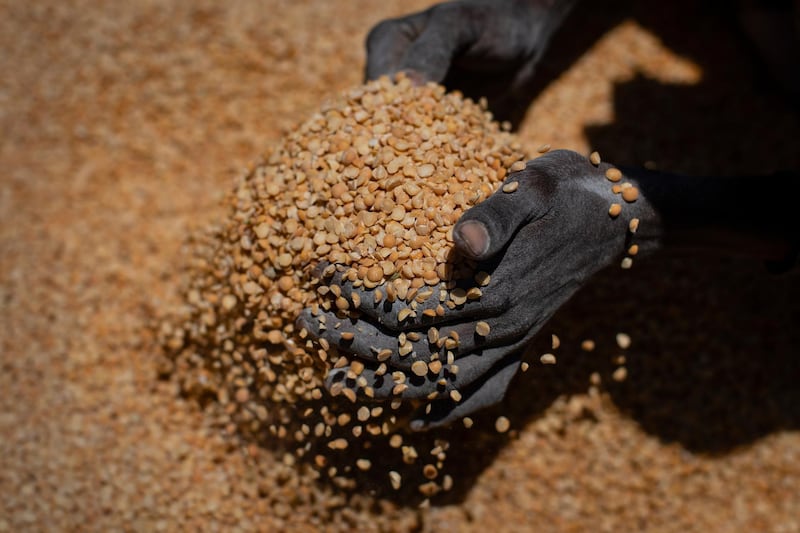
Last week, humanitarian agencies said that 350,000 people in Tigray were on the brink of famine, a crisis that several diplomats described as manmade amid allegations of forced starvation. Ethiopia's government has rejected the figure and says food aid has reached 5.2 million in the region of six million.
No date has been set for voting in Tigray’s 38 constituencies, where military personnel who usually play a key role in transporting election materials across Africa’s second-most populous country are busy with the conflict.
Meanwhile, voting has been postponed until September in 64 out of 547 constituencies across Ethiopia because of insecurity, defective ballot papers and opposition allegations of irregularities.
Outbreaks of ethnic violence have also killed hundreds of people in the Amhara, Oromia and Benishangul-Gumuz regions in recent months.
Some prominent opposition parties are boycotting the election. Others say they have been prevented from campaigning in several parts of the country.
"There have been gross violations," Yusef Ibrahim, vice president of the National Movement of Amhara, said this month. He said his party had been "effectively banned" from campaigning in several regions, with some party members arrested and banners destroyed.
Neither officials with the Prosperity Party nor Mr Abiy's office responded to requests for comment on the allegations.
Ethiopia last year postponed the election, citing the Covid-19 pandemic, adding to the tensions with Tigray's former leaders. Recently the vote was delayed again by several weeks because of technical problems involving ballot papers and a lack of polling station officials.
Mr Abiy's Prosperity Party has registered 2,432 candidates in the election, in which Ethiopians will vote for national and regional representatives. The next largest party, Ethiopian Citizens for Social Justice, is fielding 1,385 candidates. There are 47 parties contesting the election.
But on Sunday, five opposition parties released a joint statement saying that campaigning outside the capital, Addis Ababa, “has been marred by serious problems, including killings, attempted killings and beatings of candidates”.
Two prominent opposition parties, the Oromo Liberation Front and the Oromo Federalist Congress, are boycotting the vote. "It's going to be a sham election," OFC chairman Merera Gudina said.
That means the Prosperity Party will face little competition in Oromia, Ethiopia’s most populous state.
Several prominent OFC members are behind bars after a wave of unrest last year sparked by the killing of a popular Oromo musician, and the OLF's leader is under house arrest. The leader of the Balderas Party for True Democracy, Eskinder Nega, was also detained and is contesting the election from prison.
Getnet Worku, secretary general of the newly established Enat party, said this month it was not standing candidates in several constituencies because the threat of violence was too high, asserting that armed militias organised by local officials frequently broke up rallies.
There are growing international concerns over whether the elections will be fair. The European Union said it will not observe the vote after its requests to import communications equipment were denied.

In response, Ethiopia said external observers "are neither essential nor necessary to certify the credibility of an election", although it has since welcomed observers sent by the African Union.
Last week the US State Department said it was “gravely concerned about the environment under which these upcoming elections are to be held”, citing “detention of opposition politicians, harassment of independent media, partisan activities by local and regional governments, and the many inter-ethnic and inter-communal conflicts across Ethiopia“.
Mr Abiy's appointment as prime minister in 2018 was initially greeted by an outburst of optimism at home and abroad. Shortly after taking office, he freed tens of thousands of political prisoners, allowed the return of exiled opposition groups and rolled back punitive laws that targeted civil society.
In 2019 he won the Nobel Peace Prize in part for those reforms and for making peace with Eritrea by ending a long-running border stand-off.
But critics say Ethiopia's political space has begun to shrink again. The government denies the accusation.
Several prominent opposition figures accused of inciting unrest are behind bars.
While opening a sugar factory earlier this month, Mr Abiy accused “traitors” and “outsiders” of working to undermine Ethiopia.
This week his spokeswoman, Billene Seyoum, described the election as a chance for citizens to “exercise their democratic rights” and accused international media of mounting a “character assassination of the prime minister”.