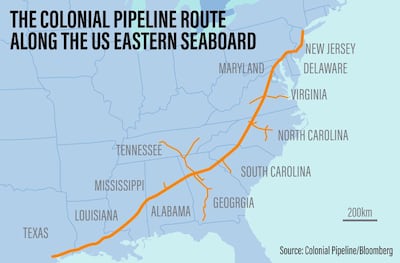
The attack on a critical US artery for the transport of fuel has once again exposed the vulnerabilities of the energy industry to cyber attacks. The ransomware attack on the 2.5 million barrels per day Colonial Pipeline endangered access to fuel for the US East Coast. The pipeline, which was built in the 1960s, snakes across a distance of 8,850 kilometres and carries products sufficient to meet the total consumption of Germany, Europe’s largest economy and the world’s fourth-biggest.
So what makes the energy industry a target for attacks and why is it vulnerable?
Any impact on the energy sector can affect entire communities and even countries. An attack on a power plant or a pipeline can cause widespread blackouts, impact transportation, heating, and the functioning of critical activities in the economy.
The vulnerability in the energy industry originates from the use of legacy industrial control systems, particularly if these have not been upgraded for a number of years and are not fully integrated across systems, according to Mohammed AlMohtadi, chief information security officer at Abu Dhabi’s Injazat.
“These legacy systems therefore not only represent risk factors for energy organisations but can also have a widespread economic impact,” he said.
So how do large energy and utility companies become prey to attacks?
Threat actors usually attempt to steal trade secrets, confidential data and intellectual property, through ransomware attacks.
“While we anticipate breaches to be very sophisticated, in most cases they occur through simple phishing emails and other social engineering activities,” added Mr AlMohtadi.
A ransomware attack, such as the one on the Colonial Pipeline, involves hackers infecting networks with malicious software that encrypts data and leaves machines locked until the victims pay an extortion fee.
On Monday, DarkSide, the group behind the attack, said its aim was to "make money" but not create problems for society. In many cases, the attacks cost the economy much more than the ransom amount demanded.
In many cases, where a cybercriminal intends to inflict political and physical damage to a country or cause financial or reputational harm, the energy sector often becomes a prime target.
“[The] energy industry comes under critical infrastructure … if it is breached, the nation's financial and physical infrastructure could be potentially crippled,” said Avinash Advani, founder and chief executive of Dubai-based cybersecurity company CyberKnight.
Oil and gas infrastructure, nuclear plants, electricity grids, water companies and utility firms that supply the community with power, water, and treat sewage are potential targets.
The Covid-19 pandemic has exposed the energy industry's underbelly. As more people work from home to contain the spread of coronavirus, they unwittingly expose an organisation to cyber attacks.
“Employees at energy organisations are working from home and remotely accessing corporate assets … [they] become a critical attack vector and entry point for attackers,” said Mr Advani.
Researchers have found many coronavirus-related malicious e-mail campaigns and hundreds of downloadable files that attempt to infect user devices. Malicious files have been masked under the guise of pdf, mp4 and docx files. The names of files imply that they contain instructions on how to protect yourself from the virus or updates on the threat.
So how did the Colonial Pipeline become victim to a cyberattack?
“We assume the Colonial Pipeline, the biggest US pipeline system connecting oil supplies in Texas with New York, has been attacked through an insecure remote access,” Stefan Schachinger, network security product manager at computer security company Barracuda, said.
“Remote accesses are not insecure per definition but require proper security measures such as encryption and multi-factor authentication,” he added.
DarkSide, the ransomware group that claimed the Colonial Pipeline attack is new but experienced, industry experts said.
The group targets largely English-speaking countries and avoids the economies of former Soviet states, said Boston-based cyber security firm Cybereason. Its ransom demand typically ranges from $200,000 to $2 million. The group has published stolen data from more than 40 victims, who are believed to be just a fraction of the overall number.
Cyber attacks on energy infrastructure are typically politically or financially motivated.
“When there is an attack on the West, it usually originates from [entities inside] Russia or Eastern European countries with ties to Russia, Iran, China, or North Korea,” said Mr Advani.
However, there can be financially motivated criminal groups that may or may not be associated with a government.
President Joe Biden has said there is no evidence that the Russian government is responsible for the attack on the Colonial Pipeline, but that the country has "some responsibility" to address the ransomware attack and that he will seek global co-operation to battle similar hacks.
US Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm told Bloomberg TV that supply in the country has so far not been impacted and that the company has said it hopes to restore operations by the end of this week.
“It tells you how utterly vulnerable we are,” Ms Granholm said. “We’re seeing all of these examples of ransomware attacks coming - whether it’s telecommunications or this critical infrastructure. And obviously in my lane I’m very worried about the energy infrastructure.”
She said the incident clearly highlighted the need of private sector companies to step up their investment in cyber defence.
Globally, around 61 per cent of companies surveyed by London-based Mimecast said they were affected by a ransomware attack last year. About 52 per cent of them paid the ransom but of those, only two-thirds recovered their data.
Given the serious implications of cyber attacks, the energy industry should not underestimate groups that target facilities. Many of these groups now have help desks, technical support, payroll processing, and subcontractors, according to Marty Edwards, vice president of operational technology security at Maryland-based cyber-security company Tenable.
“They are essentially full-fledged criminal corporations operating in the digital world.”
"If reports are accurate, the Colonial Pipeline incident has all of the markings of a possible ransomware attack that began in the IT environment and, out of precaution, forced the operator to shut down operations,” added Mr Edwards.
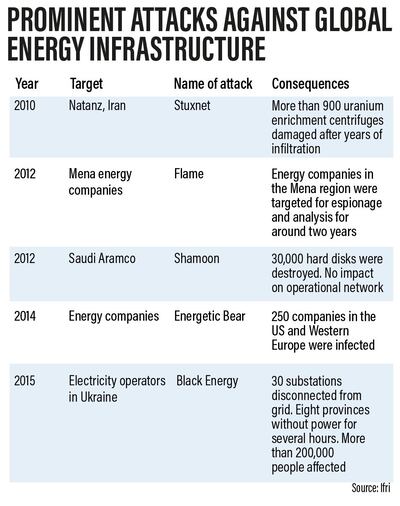
In 2012, the Shamoon virus attack on Saudi Aramco systems wiped the hard drives of some 30,000 computers clean.
The attacks were blamed on Iran, which denied responsibility.
In 2017, a $20 billion petrochemical project joint venture between Saudi Aramco and Dow Chemicals also experienced a spate of hacking attacks.
The financial fallout from cyber attacks in the Arabian Gulf in 2017 was estimated at more than $1bn, according to a 2018 report by Siemens. Three-quarters of regional oil and gas companies, or over 30 per cent of the global production of oil, have experienced some form of cyber-security breach in the past, according to DarkMatter, a UAE-based cyber security company.
The financial fallout from data breaches among a selected sample of companies in the UAE and Saudi Arabia rose 9.4 per cent, costing them $6.53m per breach, according to a 2020 study by IBM Security.
In 2017, Saudi Arabia, Opec's biggest producer, established the National Cybersecurity Authority (NCA) to combat cyber threats.
The UAE rolled out its first National Cybersecurity Strategy in 2019, followed by the formation of National Cybersecurity Council to develop policies and laws to strengthen cyber security and ensure the country is not vulnerable to attacks.
In December, Dubai Electronic Security Centre rolled out a cyber resilience plan that aims to safeguard the emirate's critical infrastructure including oil and gas sector. In June, Injazat opened a Cyber Fusion Centre in Abu Dhabi, expanding its cyber defence abilities and portfolio of services.
In the Middle East, companies such as Saudi Aramco, the world's largest exporter of oil, are enforcing stricter compliance on third-party vendors to ensure their facilities are protected against cyber attacks, that could impact the supply of oil globally.
Suppliers including general vendors and those specialising in outsourced infrastructure, customised software, network connectivity, and critical data processors need to obtain Saudi Aramco's cyber security standard certification.